How AI, IoT, and Generative AI Enable Food Protection
By Richmond Victor E. Ejanda
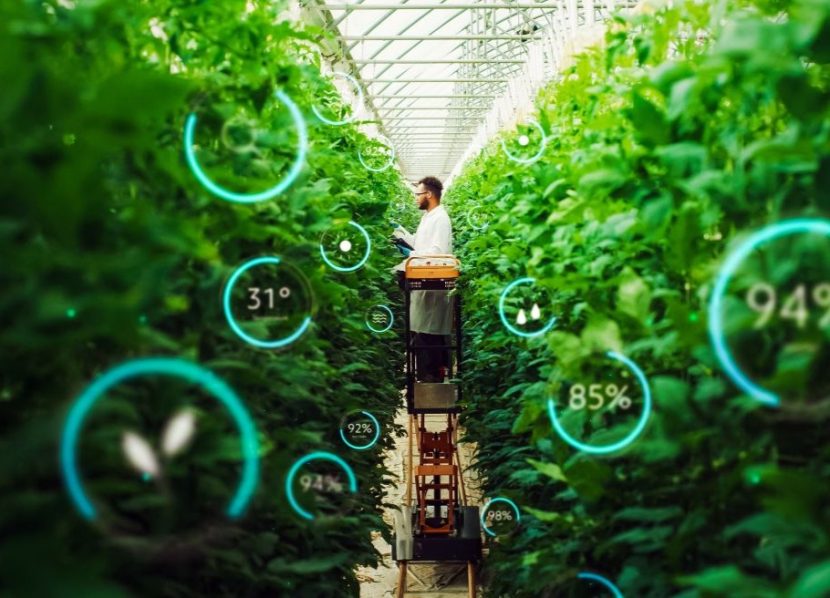
The food industry faces constant challenges in ensuring the safety and quality of products. With Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Generative AI, traditional methods of food safety management are being revolutionized. These technologies enable proactive, precise predictions to identify risks and implement corrective actions before issues occur.
The global food industry must deliver safe, high-quality products while adhering to strict regulations. Traditional food safety practices often rely on reactive measures, addressing non-compliance after an incident.
Advancements in AI, IoT, and Generative AI offer transformative solutions, enabling proactive management of food safety risks. These tools equip manufacturers, regulators, and other stakeholders with predictive, precise interventions.
Mera Fae Bundoc, Senior Regulatory Consultant of EMCF Philippines, emphasizes, “The integration of AI and IoT in food safety systems addresses the growing complexity of supply chains and ensures that risks are mitigated before they escalate. This approach is not just innovative but essential in meeting the demands of today’s fast-paced and interconnected world from postharvest handling to finished product distribution.”
AI-powered algorithms can analyze historical and real-time data to proactively identify risks like microbial contamination, reducing recalls and improving safety.
Generative AI further expands the toolkit, offering solutions previously unimaginable.
AI in Food Safety
AI transforms food safety by leveraging machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing. For instance, AI-powered algorithms can analyze historical and real-time data to proactively identify risks, such as microbial contamination, based on environmental conditions or ingredient quality. AI-enabled computer vision systems can also detect defects more accurately than traditional inspections, ensuring consistent product quality.
When it comes to supply chain optimization, AI can also enhance visibility across supply chains, flagging delays or disruptions that could compromise food safety. By interpreting regulations, generating reports, and suggesting corrective actions, human error is reduced, and compliance and safety increase.
IoT in Real-Time Monitoring
IoT complements AI with real-time data collection through sensors, cloud computing, and wireless networks. For example, IoT sensors that monitor temperature, humidity, and other conditions can prevent spoilage. Further, RFID tags and sensors enhance end-to-end supply chain traceability. IoT can also monitor equipment performance and maintenance schedules to prevent product issues linked to equipment failure. IoT-enabled cameras and devices are also able to detect foreign objects, residues, or biological contaminants in real time, enabling immediate corrective actions.
Generative AI in Food Safety
Generative AI creates data, simulations, and visualizations, expanding the capabilities of AI and IoT. Generative AI simulates data for scenarios like microbial growth under varying conditions, supporting predictive modeling when real-world data is limited. It can optimize quality control by generating synthetic images of defects or contamination to improve AI-based detection systems. Generative AI can also create simulations of outbreaks or supply chain disruptions, helping companies stress-test safety protocols. It can propose solutions like optimized facility layouts or workflows to minimize contamination risks.
On the customer side of the equation, Generative AI can analyze consumer safety concerns, aligning production protocols with expectations. These capabilities reinforce a proactive approach to address evolving food safety challenges.
Case Studies in Action
Organizations have implemented AI, IoT, and Generative AI with significant results:
- Smart Cold Chain Management: A U.S. dairy producer used IoT sensors and AI to monitor temperature in transit, reducing spoilage by 20 percent and improving compliance with regulations.
- AI-Powered Microbial Detection: A global food company used AI to analyze microbial test data, predicting contamination risks with 90 percent accuracy and reducing recalls.
- Generative AI for Risk Simulation: A multinational manufacturer simulated contamination scenarios to identify vulnerabilities and implement targeted safety measures.
Integrating these technologies addresses the complexities of modern supply chains. By combining real-time insights, predictive capabilities, and simulations, the food industry mitigates risks before they escalate. Despite benefits, challenges remain:
- High Initial Costs: Developing IoT infrastructure and AI models requires significant investment, deterring smaller enterprises.
- Data Integration and Security: Managing data from various sources and ensuring cybersecurity are complex tasks, particularly for IoT systems vulnerable to breaches.
- Regulatory Gaps: Current regulations may not fully address these technologies, creating uncertainty around compliance.
- Skill Gap: Specialized skills for implementing and maintaining these systems are limited within the food industry.
The future of AI, IoT, and Generative AI in food safety is promising. For instance, edge computing can process data at its source, reducing latency and enhancing decision-making speed, and blockchain integration improves transparency and traceability across supply chains. Utilization of Generative AI for training can also create realistic training datasets and scenarios to improve the robustness of safety systems. Advances in IoT hardware are expected to lower costs, making them accessible to small enterprises.
AI, IoT, and Generative AI are transforming food safety by enabling proactive, precise, and innovative predictions. These technologies excel in predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, traceability, and scenario simulations, offering unparalleled benefits. These tools are not just innovative but essential strategies for addressing modern challenges. With ongoing advancements in technology and regulations, these systems promise broader adoption, driving the food industry toward a safer, more sustainable, smarter future.
About the Author:
Richmond Victor E. Ejanda is a licensed food technologist and a certified management consultant with over a decade of expertise in food safety, manufacturing innovation, and regulatory compliance. He is the author of “Kuisina Gastronomika,” which was nominated as one of the Best Books on Food by the Philippine National Book Awards. He also co-authored volumes 1 and 2 of “Introduction to Food Technology” in the Philippines. He is the founder of “Food, Health & Science,” the country’s first food technology and nutrition magazine.

-
 FeaturedRisk management
The Cost of a Breach: What a Cyberattack Could Mean for Food Safety Recalls
FeaturedRisk management
The Cost of a Breach: What a Cyberattack Could Mean for Food Safety Recalls
-
 FeaturedRisk management
Securing the Food Chain: How ISO/IEC 27001 Strengthens Cybersecurity
FeaturedRisk management
Securing the Food Chain: How ISO/IEC 27001 Strengthens Cybersecurity
-
 FeaturedRisk management
Revolutionizing Food Safety Training: Breaking Out of the “Check-the-Box” Mentality
FeaturedRisk management
Revolutionizing Food Safety Training: Breaking Out of the “Check-the-Box” Mentality
-
 GFSI Standards
GFSI 2025: Building Trust, Tech-Forward Solutions, and Global Unity in Food Safety
GFSI Standards
GFSI 2025: Building Trust, Tech-Forward Solutions, and Global Unity in Food Safety
-
 FeaturedFood Safety
Integrated Pest Management: Strategies to Protect Your Brand’s Reputation
FeaturedFood Safety
Integrated Pest Management: Strategies to Protect Your Brand’s Reputation
-
 FeaturedFood Safety Culture & Training
No Open Door Policy: Challenges That Impact Pest Control in Food Processing Plants
FeaturedFood Safety Culture & Training
No Open Door Policy: Challenges That Impact Pest Control in Food Processing Plants




